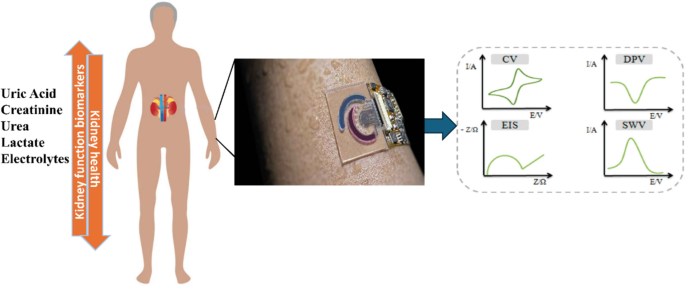
Role of wearable electrochemical biosensors in monitoring renal function biomarkers in sweat: a review

Real-time detection of renal biomarkers is crucial for immediate and continuous monitoring of kidney function, facilitating early diagnosis and intervention in kidney-related disorders. This proactive approach enables timely adjustments in treatment plans, particularly in critical situations, and enhances overall patient care. Wearable devices emerge as a promising solution, enabling non-invasive and real-time data collection. This comprehensive review investigates numerous types of wearable sensors designed to detect kidney biomarkers in body fluids such as sweat. It critically evaluates the precision, dependability, and user-friendliness of these devices, contemplating their seamless integration into daily life for continuous health tracking. The review highlights the potential influence of wearable technology on individualized renal healthcare and its role in preventative medicine while also addressing challenges and future directions. The review's goal is to provide guidance to academics, healthcare professionals, and technologists working on wearable solutions for renal biomarker detection by compiling the body of current knowledge and advancements.
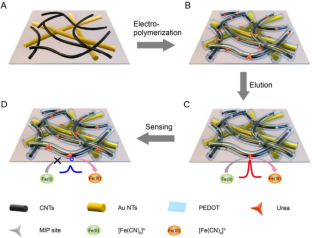
Graphical abstract
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve



Similar content being viewed by others

Sweat-Based in Vitro Diagnostics (IVD): From Sample Collection to Point-of-Care Testing (POCT)
Article 01 January 2019

Article 25 February 2019
Opportunities and challenges for sweat-based monitoring of metabolic syndrome via wearable technologies
Article Open access 18 July 2023
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
- J. Kim, A.S. Campbell, B.E.F. de Ávila, J. Wang, Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 37(4), 389–406 (2019) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- SSh.M. Ameen, I.B. Qader, H.A. Qader, F.K. Algethami, B.Y. Abdulkhair, K.M. Omer, Dual-state dual emission from precise chemically engineered bi-ligand MOF free from encapsulation and functionalization with self-calibration model for visual detection. Microchim. Acta 191(1), 62 (2023) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- J.R. Sempionatto, I. Jeerapan, S. Krishnan, J. Wang, Wearable chemical sensors: emerging systems for on-body analytical chemistry. Anal. Chem. 92(1), 378–396 (2020) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- J. Kim, R. Kumar, A.J. Bandodkar, J. Wang, Advanced materials for printed wearable electrochemical devices: a review. Adv. Electron. Mater. 3(1), 1600260 (2017) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- H. Teymourian, M. Parrilla, J.R. Sempionatto, N.F. Montiel, A. Barfidokht, R. Van Echelpoel et al., Wearable electrochemical sensors for the monitoring and screening of drugs. ACS Sens. 5(9), 2679–2700 (2020) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- J.R. Windmiller, J. Wang, Wearable electrochemical sensors and biosensors: a review. Electroanalysis 25(1), 29–46 (2013) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- B. Bikbov, C.A. Purcell, A.S. Levey, M. Smith, A. Abdoli, M. Abebe et al., Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet 395(10225), 709–733 (2020) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- F. Dieterle, F. Sistare, F. Goodsaid, M. Papaluca, J.S. Ozer, C.P. Webb et al., Renal biomarker qualification submission: a dialog between the FDA-EMEA and Predictive Safety Testing Consortium. Nat. Biotechnol. 28(5), 455–462 (2010) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- L.H. Lash, Cellular and functional biomarkers of renal injury and disease. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 31, 100348 (2022) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- B. Unadike, Commentary on the burden of chronic kidney disease. Ibom Med. J. 5, 1–2 (2012) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- P. Agre, G.M. Preston, B.L. Smith, J.S. Jung, S. Raina, C. Moon et al., Aquaporin CHIP: the archetypal molecular water channel. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 265(4), F463–F476 (1999) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- D.R. Finco, Chapter 17 - Kidney function, in Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals (Fifth Edition). ed. by J.J. Kaneko, J.W. Harvey, M.L. Bruss (Academic Press, San Diego, 1997), pp.441–484 ChapterGoogle Scholar
- S.P. Mohanty, E. Kougianos, Biosensors: a tutorial review. IEEE Potentials 25(2), 35–40 (2006) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- F. Ghasemi, N. Fahimi-Kashani, A. Bigdeli, A.H. Alshatteri, S. Abbasi-Moayed, S.H. Al-Jaf et al., Paper-based optical nanosensors – a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 1238, 340640 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Y. Lee, J. Kim, H. Joo, M.S. Raj, R. Ghaffari, D.H. Kim, Wearable sensing systems with mechanically soft assemblies of nanoscale materials. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2(9), 1700053 (2017) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- J. Xie, Q. Chen, H. Shen, G. Li, Review—Wearable graphene devices for sensing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167(3), 037541 (2020) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- S.M.A. Iqbal, I. Mahgoub, E. Du, M.A. Leavitt, W. Asghar, Advances in healthcare wearable devices. npj Flex. Electron. 5(1), 1–14 (2021) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- J.V. Vaghasiya, C.C. Mayorga-Martinez, M. Pumera, Wearable sensors for telehealth based on emerging materials and nanoarchitectonics. npj Flex. Electron. 7(1), 1–14 (2023) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- L. Qiao, M.R. Benzigar, J.A. Subramony, N.H. Lovell, G. Liu, Advances in sweat wearables: sample extraction, real-time biosensing, and flexible platforms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(30), 34337–34361 (2020) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- C.H. Chen, P.W. Lee, Y.H. Tsao, Z.H. Lin, Utilization of self-powered electrochemical systems: metallic nanoparticle synthesis and lactate detection. Nano Energy 42, 241–248 (2017) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- A.J. Bandodkar, W.J. Jeang, R. Ghaffari, J.A. Rogers, Wearable sensors for biochemical sweat analysis. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 12(1), 1–22 (2019) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- N.D. Zakaria, H.H. Hamzah, I.L. Salih, V. Balakrishnan, R.K. Abdul, A Review of detection methods for vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) genes: from conventional approaches to potentially electrochemical DNA biosensors. Biosensors 13(2), 294 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- K.M. Omer, A.L. Kanibolotsky, P.J. Skabara, I.F. Perepichka, A.J. Bard, Electrochemistry, spectroscopy, and electrogenerated chemiluminescence of some star-shaped truxene-oligofluorene compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 111(24), 6612–6619 (2007) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- I.H. Cho, D.H. Kim, S. Park, Electrochemical biosensors: perspective on functional nanomaterials for on-site analysis. Biomater. Res. 24(1), 6 (2020) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- M. Pohanka, P. Skládal, Electrochemical biosensors—principles and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 6, 57–64 (2008) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- K.M. Omer, S.Y. Ku, Y.C. Chen, K.T. Wong, A.J. Bard, Electrochemical behavior and electrogenerated chemiluminescence of star-shaped D-A compounds with a 1,3,5-triazine core and substituted fluorene arms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(31), 10944–10952 (2010) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Y. Wang, H. Xu, J. Zhang, G. Li, Electrochemical sensors for clinic analysis. Sensors 8(4), 2043–2081 (2008) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- P. Batista Deroco, J.D.F. Giarola, D. Wachholz Júnior, G. Arantes Lorga, Kubota L. Tatsuo, Chapter Four - Paper-based electrochemical sensing devices, in Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, vol. 89, ed. by A. Merkoçi (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2020), pp.91–137 Google Scholar
- J. Ding, W. Qin, Recent advances in potentiometric biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 124, 115803 (2020) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- M. Parrilla, J. Ferré, T. Guinovart, F.J. Andrade, Wearable potentiometric sensors based on commercial carbon fibres for monitoring sodium in sweat. Electroanalysis 28(6), 1267–1275 (2016) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Q. An, S. Gan, J. Xu, Y. Bao, T. Wu, H. Kong et al., A multichannel electrochemical all-solid-state wearable potentiometric sensor for real-time sweat ion monitoring. Electrochem. Commun. 107, 106553 (2019) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- G. Ibáñez-Redín, G. Cagnani, N. Gomes, P. Raymundo-Pereira, S. Machado, M. AntonioGutierrez et al., Wearable potentiometric biosensor for analysis of urea in sweat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 223, 114994 (2022) ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- S. Bilal, Cyclic voltammetry, in Encyclopedia of Applied Electrochemistry. ed. by G. Kreysa, K.I. Ota, R.F. Savinell (Springer, 2014), pp.285–289 ChapterGoogle Scholar
- S.B. Adeloju, Amperometry, in Encyclopedia of Analytical Science (Second Edition). ed. by P. Worsfold, A. Townshend, C. Poole (Elsevier, 2005), pp.70–79 ChapterGoogle Scholar
- M. Lovrić, Square-wave voltammetry, in Electroanalytical Methods: Guide to Experiments and Applications. ed. by F. Scholz, A.M. Bond, R.G. Compton, D.A. Fiedler, G. Inzelt, H. Kahlert et al. (Springer, 2010), pp.121–145 ChapterGoogle Scholar
- V. Mirceski, R. Gulaboski, M. Lovric, I. Bogeski, R. Kappl, M. Hoth, Square-wave voltammetry: a review on the recent progress. Electroanalysis 25(11), 2411–2422 (2013) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- J. Yoon, M. Sim, T.S. Oh, Y.S. Yoon, D.J. Kim, Flexible electrochemical sensor based on NiCu(OOH) for monitoring urea in human sweat. J. Electrochem. Soc. 168(11), 117510 (2021) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Y. Chen, G. Li, W. Mu, X. Wan, D. Lu, J. Gao et al., Nonenzymatic sweat wearable uric acid sensor based on N-doped reduced graphene oxide/Au dual aerogels. Anal. Chem. 95(7), 3864–3872 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wiley.com, Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd edn. (Wiley, 2024)
- M.S. Belluzo, M.E. Ribone, C.M. Lagier, Assembling amperometric biosensors for clinical diagnostics. Sensors 8(3), 1366–1399 (2008) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- P. Kassal, J. Kim, R. Kumar, W.R. de Araujo, I.M. Steinberg, M.D. Steinberg et al., Smart bandage with wireless connectivity for uric acid biosensing as an indicator of wound status. Electrochem. Commun. 56, 6–10 (2015) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- B. Gil, S. Anastasova, G.Z. Yang, A smart wireless ear-worn device for cardiovascular and sweat parameter monitoring during physical exercise: design and performance results. Sensors 19(7), 1616 (2019) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- J. Baranwal, B. Barse, G. Gatto, G. Broncova, A. Kumar, Electrochemical sensors and their applications: a review. Chemosensors. 10(9), 363 (2022) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- M.L. Yahaya, R. Noordin, Razak K. Abdul, Chapter 1 - Advanced nanoparticle-based biosensors for diagnosing foodborne pathogens, in Advanced Biosensors for Health Care Applications. ed. by A. Inamuddin, R. Khan, A. Mohammad, A.M. Asiri (Elsevier, 2019), pp.1–43 Google Scholar
- D. Khodagholy, V.F. Curto, K.J. Fraser, M. Gurfinkel, R. Byrne, D. Diamond et al., Organic electrochemical transistor incorporating an ionogel as a solid state electrolyte for lactate sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 22(10), 4440–4443 (2012) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- C.S. Pundir, S. Jakhar, V. Narwal, Determination of urea with special emphasis on biosensors: a review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 123, 36–50 (2019) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- T. Liu, X. Liu, Perspectives in wearable systems in the human-robot interaction (HRI) field. Sensors 23(19), 8315 (2023) ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Y.L. Liu, R. Liu, Y. Qin, Q.F. Qiu, Z. Chen, S.B. Cheng et al., Flexible electrochemical urea sensor based on surface molecularly imprinted nanotubes for detection of human sweat. Anal. Chem. 90(21), 13081–13087 (2018) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- N. Promphet, W. Phamonpon, W. Karintrithip, P. Rattanawaleedirojn, K. Saengkiettiyut, Y. Boonyongmaneerat et al., Carbonization of self-reduced AuNPs on silk as wearable skin patches for non-invasive sweat urea detection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 242(Pt 2), 124757 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Z. Li, Y. Wang, Z. Fan, Y. Sun, Y. Sun, Y. Yang et al., A dual-function wearable electrochemical sensor for uric acid and glucose sensing in sweat. Biosensors 13(1), 105 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Y. Yang, Y. Song, X. Bo, J. Min, O.S. Pak, L. Zhu et al., A laser-engraved wearable sensor for sensitive detection of uric acid and tyrosine in sweat. Nat. Biotechnol. 38(2), 217–224 (2020) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- X. Liu, P.B. Lillehoj, Embroidered electrochemical sensors on gauze for rapid quantification of wound biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 98, 189–194 (2017) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Z. Xu, J. Song, B. Liu, S. Lv, F. Gao, X. Luo et al., A conducting polymer PEDOT:PSS hydrogel based wearable sensor for accurate uric acid detection in human sweat. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 348, 130674 (2022) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- X. Wei, M. Zhu, J. Li, L. Liu, J. Yu, Z. Li et al., Wearable biosensor for sensitive detection of uric acid in artificial sweat enabled by a fiber structured sensing interface. Nano Energy 85, 106031 (2021) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- S. RoyChoudhury, Y. Umasankar, J. Jaller, I. Herskovitz, J. Mervis, E. Darwin et al., Continuous monitoring of wound healing using a wearable enzymatic uric acid biosensor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 165(8), B3168 (2018) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- J. Xiao, Y. Luo, L. Su, J. Lu, W. Han, T. Xu et al., Hydrophilic metal-organic frameworks integrated uricase for wearable detection of sweat uric acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 1208, 339843 (2022) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- A. Singh, A. Sharma, S. Arya, Deposition of Ni/RGO nanocomposite on conductive cotton fabric as non-enzymatic wearable electrode for electrochemical sensing of uric acid in sweat. Diam. Relat. Mater. 130, 109518 (2022) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Y. Zhang, C. Hou, P. Zhao, X. Zeng, Y. Liu, J. Chen et al., Fe single-atom nanozyme-modified wearable hydrogel patch for precise analysis of uric acid at rest. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15(37), 43541–43549 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- P. Raymundo-Pereira, N. Gomes, S.A.S. Machado, O. Oliveira, Wearable glove-embedded sensors for therapeutic drug monitoring in sweat for personalized medicine. Chem. Eng. J. 435, 135047 (2022) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Y. Hu, L. Wang, J. Li, Y. Yang, G. Zhao, Y. Liu et al., Thin, soft, skin-integrated electronics for real-time and wireless detection of uric acid in sweat. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 14, 1–14 (2023) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- R.R. Silva, P.A. Raymundo-Pereira, A.M. Campos, D. Wilson, C.G. Otoni, H.S. Barud et al., Microbial nanocellulose adherent to human skin used in electrochemical sensors to detect metal ions and biomarkers in sweat. Talanta 218, 121153 (2020) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- V. Kammarchedu, D. Butler, A. Ebrahimi, A machine learning-based multimodal electrochemical analytical device based on eMoSx-LIG for multiplexed detection of tyrosine and uric acid in sweat and saliva. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1232, 340447 (2022) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- F. Vivaldi, A. Dallinger, N. Poma, A. Bonini, D. Biagini, P. Salvo et al., Sweat analysis with a wearable sensing platform based on laser-induced graphene. APL Bioeng. 6(3), 036104 (2022) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- L. Yang, H. Wang, A.M. Abdullah, C. Meng, X. Chen, A. Feng et al., Direct laser writing of the porous graphene foam for multiplexed electrochemical sweat sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 34332–34342 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- X. Qiao, Y. Cai, Z. Kong, Z. Xu, X. Luo, A wearable electrochemical sensor based on anti-fouling and self-healing polypeptide complex hydrogels for sweat monitoring. ACS Sens. 8, 2834–2842 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- H. Lin, J. Tan, J. Zhu, S. Lin, Y. Zhao, W. Yu et al., A programmable epidermal microfluidic valving system for wearable biofluid management and contextual biomarker analysis. Nat. Commun. 11, 4405 (2020) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- M. Asaduzzaman, M.A. Zahed, M. Sharifuzzaman, M.S. Reza, X. Hui, S. Sharma et al., A hybridized nano-porous carbon reinforced 3D graphene-based epidermal patch for precise sweat glucose and lactate analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 219, 114846 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- X. Luo, L. Guo, Y. Liu, W. Shi, W. Gai, Y. Cui, Wearable tape-based smart biosensing systems for lactate and glucose. IEEE Sens. J. 20(7), 3757–3765 (2020) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- M. Li, L. Wang, R. Liu, J. Li, Q. Zhang, G. Shi et al., A highly integrated sensing paper for wearable electrochemical sweat analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 174, 112828 (2020) ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- A. Bhide, K.C. Lin, S. Muthukumar, S. Prasad, On-demand lactate monitoring towards assessing physiological responses in sedentary populations. The Analyst 6, 146 (2021) Google Scholar
- X. Xuan, C. Pérez-Ràfols, C. Chen, M. Cuartero, G.A. Crespo, Lactate biosensing for reliable on-body sweat analysis. ACS Sens. 6(7), 2763–2771 (2021) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- T. Saha, T. Songkakul, C.T. Knisely, M.A. Yokus, M.A. Daniele, M.D. Dickey et al., Wireless wearable electrochemical sensing platform with zero-power osmotic sweat extraction for continuous lactate monitoring. ACS Sens. 7(7), 2037–2048 (2022) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- S. Santiago-Malagón, D. Río-Colín, H. Azizkhani, M. Aller-Pellitero, G. Guirado, F.J. Del Campo, A self-powered skin-patch electrochromic biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 175, 112879 (2021) ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- L. Meng, A.P.F. Turner, W.C. Mak, Conducting polymer-reinforced laser-irradiated graphene as a heterostructured 3D transducer for flexible skin patch biosensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(45), 54456–54465 (2021) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- A.J. Bandodkar, P. Gutruf, J. Choi, K. Lee, Y. Sekine, J.T. Reeder et al., Battery-free, skin-interfaced microfluidic/electronic systems for simultaneous electrochemical, colorimetric, and volumetric analysis of sweat. Sci. Adv. 5(1), eaav3294 (2019) ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- J. Dieffenderfer, M. Wilkins, C. Hood, E. Beppler, M.A. Daniele, A. Bozkurt, Towards a sweat-based wireless and wearable electrochemical sensor, in 2016 IEEE Sensors (2016), pp. 1–3
- Q. Zhang, D. Jiang, C. Xu, Y. Ge, X. Liu, Q. Wei et al., Wearable electrochemical biosensor based on molecularly imprinted Ag nanowires for noninvasive monitoring lactate in human sweat. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 320, 128325 (2020) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- R. Wang, Q. Zhai, T. An, S. Gong, W. Cheng, Stretchable gold fiber-based wearable textile electrochemical biosensor for lactate monitoring in sweat. Talanta 222, 121484 (2020) ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- M.A. Yokus, T. Saha, J. Fang, M.D. Dickey, O.D. Velev, M.A. Daniele, Towards wearable electrochemical lactate sensing using osmotic-capillary microfluidic pumping, in 2019 IEEE Sensors (2019), pp. 1–4
- M. Yu, Y.T. Li, Y. Hu, L. Tang, F. Yang, W.L. Lv et al., Gold nanostructure-programmed flexible electrochemical biosensor for detection of glucose and lactate in sweat. J. Electroanal. Chem. 882, 115029 (2021) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- H.Y.Y. Nyein, L.C. Tai, Q.P. Ngo, M. Chao, G.B. Zhang, W. Gao et al., A wearable microfluidic sensing patch for dynamic sweat secretion analysis. ACS Sens. 3(5), 944–952 (2018) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- C. Zhao, X. Li, Q. Wu, X. Liu, A thread-based wearable sweat nanobiosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 188, 113270 (2021) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- J. Wang, L. Wang, G. Li, D. Yan, C. Liu, T. Xu et al., Ultra-small wearable flexible biosensor for continuous sweat analysis. ACS Sens. 7(10), 3102–3107 (2022) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- V. Rajendran, T. Nakagawa, J. Mathiyarasu, A.M. Mohan, Fully printed wearable microfluidic devices for high-throughput sweat sampling and multiplexed electrochemical analysis. ACS Sens. 6, 1174–1186 (2021) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- X. Cui, Y. Bao, T. Han, L. Zhenbang, Y. Ma, Z. Sun, A wearable electrochemical sensor based on β-CD functionalized graphene for pH and potassium ion analysis in sweat. Talanta 245, 123481 (2022) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- X. Mei, J. Yang, J. Liu, Y. Li, Wearable, nanofiber-based microfluidic systems with integrated electrochemical and colorimetric sensing arrays for multiplex sweat analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 454, 140248 (2023) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- F. Lopresti, B. Patella, V. Divita, C. Zanca, L. Botta, N. Radacsi et al., Green and integrated wearable electrochemical sensor for chloride detection in sweat. Sensors (Basel) 22(21), 8223 (2022) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- J. Kim, W.R. De Araujo, I.A. Samek, A.J. Bandodkar, W. Jia, B. Brunetti et al., Wearable temporary tattoo sensor for real-time trace metal monitoring in human sweat. Electrochem. Commun. 51, 41–45 (2015) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- N. Coppedè, M. Giannetto, M. Villani, V. Lucchini, E. Battista, M. Careri et al., Ion selective textile organic electrochemical transistor for wearable sweat monitoring. Org. Electron. 78, 105579 (2020) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- H.Y.Y. Nyein, W. Gao, Z. Shahpar, S. Emaminejad, S. Challa, K. Chen et al., A wearable electrochemical platform for noninvasive simultaneous monitoring of Ca2+ and pH. ACS Nano 10(7), 7216–7224 (2016) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- A. Ghoorchian, M. Kamalabadi, M. Moradi, T. Madrakian, A. Afkhami, H. Bagheri et al., Wearable potentiometric sensor based on Na0.44MnO2 for non-invasive monitoring of sodium ions in sweat. Anal. Chem. 94, 2263–2270 (2022) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- P. Pirovano, M. Dorrian, A. Shinde, A. Donohoe, A. Brady, N. Moyna et al., A wearable sensor for the detection of sodium and potassium in human sweat during exercise. Talanta 219, 121145 (2020) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Y. Gai, E. Wang, M. Liu, L. Xie, Y. Bai, Y. Yang et al., A self-powered wearable sensor for continuous wireless sweat monitoring. Small Methods. 6(10), 2200653 (2022) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- H. Liu, Z. Gu, Q. Zhao, S. Li, X. Ding, X. Xiao et al., Printed circuit board integrated wearable ion-selective electrode with potential treatment for highly repeatable sweat monitoring. Sens. Actuators, B: Chem. 355, 131102 (2022) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- S. Kalasin, P. Sangnuang, Multiplex wearable electrochemical sensors fabricated from sodiated polymers and Mxene nanosheet to measure sodium and creatinine levels in sweat. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 6(19), 18209–18221 (2023) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- T. Kim, Q. Yi, E. Hoang, R. Esfandyarpour, A 3D printed wearable bioelectronic patch for multi-sensing and in situ sweat electrolyte monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 6(4), 2001021 (2021) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- M. Joffe, C.Y. Hsu, H.I. Feldman, M. Weir, J.R. Landis, L.L. Hamm, Variability of creatinine measurements in clinical laboratories: results from the CRIC study. Am. J. Nephrol. 31(5), 426–434 (2010) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- R.K. Rakesh Kumar, M.O. Shaikh, C.H. Chuang, A review of recent advances in non-enzymatic electrochemical creatinine biosensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 1183, 338748 (2021) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- K. Sato, W.H. Kang, K. Saga, K.T. Sato, Biology of sweat glands and their disorders. I. Normal sweat gland function. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 20(4), 537–563 (1989) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- A.J. Bandodkar, I. Jeerapan, J. Wang, Wearable chemical sensors: present challenges and future prospects. ACS Sens. 1(5), 464–482 (2016) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- S. Kalasin, P. Sangnuang, W. Surareungchai, Satellite-based sensor for environmental heat-stress sweat creatinine monitoring: the remote artificial intelligence-assisted epidermal wearable sensing for health evaluation. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 7, 322–334 (2020) ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- K. Ji, S. Xia, X. Sang, A.M. Zeid, A. Hussain, J. Li et al., Enhanced luminol chemiluminescence with oxidase-like properties of FeOOH nanorods for the sensitive detection of uric acid. Anal. Chem. 95(6), 3267–3273 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- T. McGregor, S. Jones, Fluid and electrolyte problems in renal dysfunction. Anaesth. Intensiv. Care Med. 22(7), 406–409 (2021) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Z. Zhao, Q. Li, L. Chen, Y. Zhao, J. Gong, Z. Li et al., A thread/fabric-based band as a flexible and wearable microfluidic device for sweat sensing and monitoring. Lab Chip 21(5), 916–932 (2021) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- H. Yang, Y. Ji, K. Shen, Y. Qian, C. Ye, Simultaneous detection of urea and lactate in sweat based on a wearable sweat biosensor. Biomed. Opt. Express 15(1), 14–27 (2023) ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- S.M. Pirot, K.M. Omer, A.H. Alshatteri, G.K. Ali, O.B.A. Shatery, Dual-template molecularly surface imprinted polymer on fluorescent metal-organic frameworks functionalized with carbon dots for ascorbic acid and uric acid detection. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 291, 122340 (2023) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- A.H. Alshatteri, G.K. Ali, K.M. Omer, Enhanced peroxidase-mimic catalytic activity via cerium doping of strontium-based metal-organic frameworks with design of a smartphone-based sensor for on-site salivary total antioxidant capacity detection in lung cancer patients. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15(17), 21239–21251 (2023) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- SSh. Mohammed Ameen, K.M. Omer, Temperature-resilient and sustainable Mn-MOF oxidase-like nanozyme (UoZ-4) for total antioxidant capacity sensing in some citrus fruits: breaking the temperature barrier. Food Chem. 448, 139170 (2024) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- SSh. Mohammed Ameen, K.M. Omer, Recent advances of bimetallic-metal organic frameworks: preparation, properties, and fluorescence-based biochemical sensing applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 16(25), 31895–31921 (2024) ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- P.B. Hassan, S.S.M. Ameen, L. Mohammed, S.M.M. Ameen, K.M. Omer, Enhanced antibacterial activity of a novel silver-based metal organic framework towards multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumonia. Nanoscale Adv. 6, 3801–3808 (2024) ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- A.H. Alshatteri, K.M. Omer, Dual-nanocluster of copper and silver as a ratiometric-based smartphone-assisted visual detection of biothiols. Microchem. J. 187, 108385 (2023) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- S.M. Pirot, K.M. Omer, Designing of robust and sensitive assay via encapsulation of highly emissive and stable blue copper nanocluster into zeolitic imidazole framework (ZIF-8) with quantitative detection of tetracycline. J Anal Sci Technol. 13(1), 22 (2022) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- S.M. Pirot, K.M. Omer, Surface imprinted polymer on dual emitting MOF functionalized with blue copper nanoclusters and yellow carbon dots as a highly specific ratiometric fluorescence probe for ascorbic acid. Microchem. J. 182, 107921 (2022) ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- A. Bernabé-Ortiz, J.H. Zafra-Tanaka, M. Moscoso-Porras, R. Sampath, B. Vetter, J.J. Miranda et al., Diagnostics and monitoring tools for noncommunicable diseases: a missing component in the global response. Glob. Health 17(1), 26 (2021) ArticleGoogle Scholar
Funding
This work received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.














